The Remarkable Canine Sense of Smell
Superior Olfactory Capabilities
Dogs have an incredible sense of smell that far surpasses human capabilities. Their noses contain between 220 to 300 million olfactory receptors, whereas humans only have about 5 to 6 million. This massive difference gives dogs their unparalleled ability to detect and differentiate a myriad of scents in their environment.
Moreover, the olfactory bulb in dogs’ brains, which processes smell, is 40 times larger than that of humans. This expansive olfactory bulb allows dogs to analyze and interpret complex scent profiles efficiently, making them exceptionally suited for tracking and detection tasks.
Detecting Human Scent Signatures
One of the most fascinating aspects of a dog’s olfactory prowess is its ability to identify human scent signatures. Human scent comprises a unique mixture of elements such as skin flakes, sweat, sebum, and bacterial byproducts. Each person has a distinct odor profile, almost like a fingerprint, which allows trained dogs to identify and follow specific individuals even in crowded or challenging environments.
Dogs can detect these unique scent signatures at extremely low concentrations, a skill that’s vital for search-and-rescue (SAR) operations. For instance, even tiny particles and residues left behind by a person can be picked up by a SAR dog’s finely tuned nose, enabling them to track individuals over considerable distances and time periods.
Olfactory System Complexity
The complexity of a dog’s olfactory system is truly remarkable. Their nasal anatomy is designed to maximize airflow and scent detection. When a dog sniffs, the air flows through a unique labyrinth of turbinates that increases the surface area within the nose, allowing more time for the scent particles to come into contact with the olfactory receptors.
Additionally, dogs have a specialized organ called Jacobson’s organ (or the vomeronasal organ) that detects pheromones. This capability adds another layer of scent detection that humans do not possess, further enhancing their ability to track and identify individuals based on subtle scent cues.
Transition to Human Scent Composition
Understanding the intricacies of a dog’s sense of smell enhances our appreciation of their tracking capabilities. As we delve deeper into the science of human scent composition, we will uncover how SAR dogs transform this scent detection ability into life-saving skills. With such advanced olfactory faculties, these canine heroes continue to play an indispensable role in search-and-rescue missions worldwide.
Understanding Human Scent Composition
Human scent is a fascinating and complex mixture, making each individual’s odor unique. This distinct scent composition arises from a combination of skin flakes, sweat, sebum, and bacterial byproducts. For search-and-rescue (SAR) dogs, understanding and identifying these components are crucial to their tracking success.
Components of Human Scent
Human scent is composed of several elements that contribute to its uniqueness:
- Skin Flakes: Every day, humans shed millions of microscopic skin cells. These flakes carry a person’s unique scent due to the combination of natural oils, sweat, and other secretions that adhere to the skin.
- Sweat: Both eccrine and apocrine glands produce sweat, which contains water, salts, and organic compounds. This sweat evaporates and leaves behind scent traces that SAR dogs can follow.
- Sebum: This oily substance, produced by sebaceous glands, coats the skin and hair. It helps retain moisture and adds to an individual’s scent profile.
- Bacterial Byproducts: The human body hosts a plethora of bacteria that thrive on skin and in sweat. These microorganisms produce unique byproducts through their metabolic processes, contributing to one’s distinct odor.
Unique Odor Profiles
Just like fingerprints, each person has an individual scent signature. This unique odor profile allows trained SAR dogs to distinguish one person from another, even in crowded environments. Dogs are exceptionally adept at recognizing and remembering specific scents, which they can use to track individuals over various terrains.
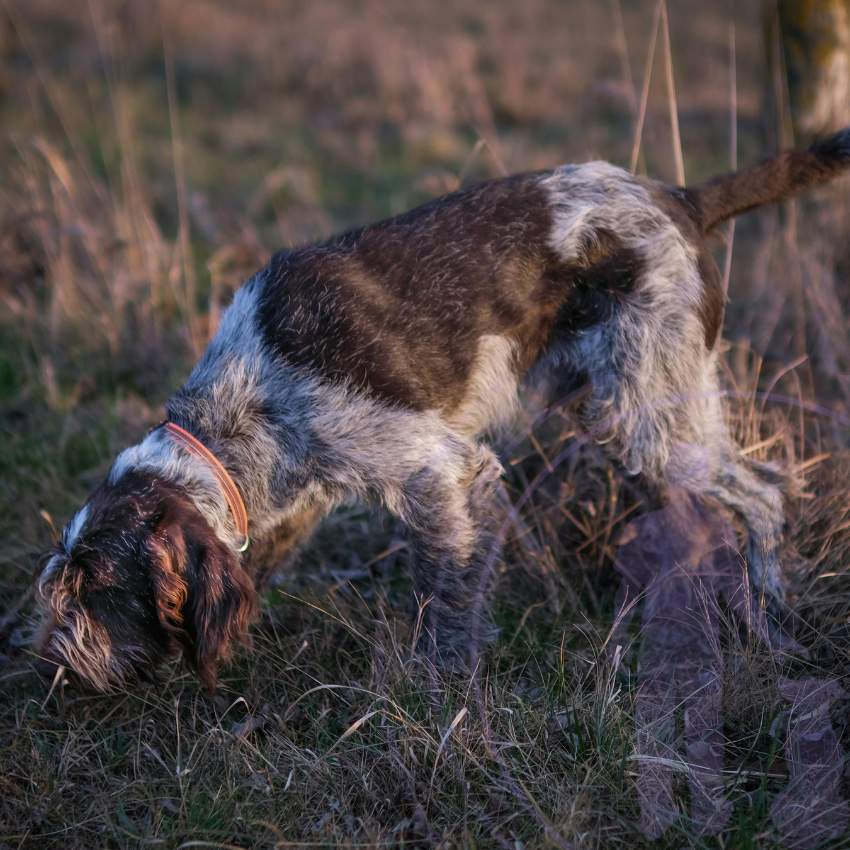

Scent Detection Over Distance and Time
Interestingly, human scent signatures can be detected over significant distances and time periods. Trained SAR dogs have the ability to follow a scent trail that may be several hours or even days old. Factors such as wind direction, temperature, and humidity can influence the dispersal and longevity of these scent particles. However, SAR dogs are trained to adapt and compensate for these environmental variables, allowing them to maintain their tracking effectiveness.
SAR dogs’ remarkable ability to understand and distinguish human scent compositions underscores their critical role in search and rescue operations. Their skills are honed through rigorous training, enabling them to traverse diverse and challenging conditions to locate missing individuals quickly.
By understanding the intricate nature of human scent and the factors influencing its detection, handlers can better prepare SAR dogs for the realities of fieldwork. Additionally, this knowledge helps to refine training programs and improve the effectiveness of these canine heroes in real-world scenarios.
Tracking Methods Used by SAR Dogs
When it comes to search and rescue (SAR) operations, dogs rely on their heightened sense of smell to trace human scent. Let’s dive into the primary techniques used by SAR dogs to track human scent effectively.
Air-Scenting Technique
Air-scenting is an incredible method where SAR dogs carry out their detective work by sniffing the airborne scent particles. This technique proves particularly useful in open areas, disaster sites, and even over bodies of water. With their noses held high, dogs can detect the faintest traces of human scent particles that the wind carries across large distances.
Air-scenting is most effective when there’s a need to search for individuals in vast, open spaces. The key advantage is that the dog doesn’t require a distinct starting point as it can pick up scents carried through the air. This method is mainly employed when it’s unknown where the person might have traveled, and it’s vital during disaster response, wilderness rescue missions, and even instances involving waterborne scent detection.
Ground Tracking Method
Ground tracking, unlike air-scenting, involves dogs following a specific human scent trail left on the ground. This method is often used in forests, urban areas, and other wilderness settings. The dog’s nose stays closer to the ground, meticulously tracing the footprint odors along surfaces.
Ground tracking relies on the scent deposited by the physical contact of someone’s footsteps – think of it as a path of human breadcrumbs. This method is particularly effective when there’s a clear starting point or last known location, providing the SAR dog with a specific trail to follow. The type of ground surface can significantly affect how well scents are retained, with grass and soft soil holding scent better than concrete or asphalt.
Combining Both Methods
There are situations where the combination of air-scenting and ground tracking becomes crucial for SAR success. Environmental conditions and the nature of the search may necessitate a flexible approach, combining both techniques. For instance, a dog may begin by ground tracking in a forest and switch to air-scenting once it reaches an open field where the scent trail might be less distinct on the surface but more detectable in the air.
Dogs are trained to adapt their scent tracking methods based on the changes in the environment, ensuring that they can pivot and continue their search effectively. This adaptability ensures that no matter the scenario, SAR dogs maintain their efficiency and effectiveness in locating missing individuals.
Understanding the fundamental methods used by SAR dogs is crucial in appreciating the intricate dance between these highly skilled canines and their handlers. We have explored how dogs harness their extraordinary olfactory abilities to track human scent, whether it is through the air or the ground. Next, we’ll delve into the myriad of environmental factors that can impact the effectiveness of scent tracking.
Environmental Factors Affecting Scent Tracking
Search and Rescue (SAR) dogs are remarkable in their ability to track human scent, but their success is greatly influenced by various environmental factors. By understanding how these factors impact the scent tracking process, SAR handlers can refine their strategies and improve search efficiencies.
Temperature and Humidity
Temperature and humidity play crucial roles in how scents are preserved and detected. In warmer and more humid conditions, scent particles tend to remain intact for longer periods. The moisture in the air helps to keep the scent particles from dissipating quickly, making it easier for dogs to pick up on and follow the trail. Conversely, in extremely dry conditions, scent particles can evaporate faster, reducing the ability for dogs to detect them effectively.
- Warm and Humid Conditions: These are ideal for scent preservation. The combination of heat and moisture helps to “lock” scent particles in the environment [Rivera & Meyers-Manor, 2024].
- Cold and Dry Conditions: Scent particles can become sparse and hard to detect, as the lack of moisture causes them to dry out and disperse faster [Pickersgill et al., 2023].
Wind Direction and Speed
Wind is another significant factor that can influence scent tracking. The wind can carry scent particles over long distances, but it can also make the scent trail unpredictable. A gust of wind can shift the scent trail, making it challenging for the dog to maintain a consistent path.
- Calm Wind: Ensures that the scent trail remains more concentrated and easier to follow.
- Variable Wind: Makes the scent disperse over a broader area, creating a more challenging situation for the dog, as the concentration of scent particles reduces with the distance they are carried.
Terrain Types
Different ground surfaces can affect how well scents are retained and how easily they can be detected. Some terrains can trap scent particles better than others, influencing the dog’s ability to track the scent accurately.
- Forests and Grasslands: These environments generally hold onto scent particles well because the vegetation can trap the particles, making it easier for dogs to detect and follow the trail.
- Rocky and Sandy Surfaces: These types of terrain can complicate scent retention as the particles can get buried or dispersed quickly. Air-scenting methods become more effective in such scenarios.
- Urban Areas: Concrete and asphalt can reflect heat, affecting the volatility and retention of scent particles. Further, urban areas present the added challenge of cross-contamination from heavy foot traffic, vehicles, and other urban elements.
Understanding these environmental factors enables SAR teams to adapt their strategies in real-time. SAR dogs’ ability to track scents effectively under varying conditions is testament to their versatility and training. By considering elements like temperature, humidity, wind, and terrain, SAR handlers can better deploy their canine partners in search missions.
SAR handlers are continually exploring ways to support dogs in overcoming environmental challenges. This involves integrating advanced tools and technologies, setting the groundwork for future innovations.
SAR Dog Training and Development
Training search and rescue (SAR) dogs is an intricate and dedicated process, beginning as early as 8 weeks old. This early start is crucial for shaping their exceptional abilities, geared towards making them reliable in high-stakes situations.
Early Scent Recognition Exercises
From around 8 weeks old, SAR puppies engage in scent recognition exercises. During this period, they are introduced to specific human odor samples in controlled environments, fostering familiarity with diverse scent profiles. This foundational training is vital to stimulate their olfactory capabilities and equip them with preliminary scent tracking skills.
Rigorous Scent Discrimination and Environmental Adaptation
Once the puppies have adapted to initial scent training, they progress to more challenging exercises that focus on scent discrimination and environmental adaptation.
Scent Discrimination Training
Training dogs to differentiate between various scents is a core aspect. SAR dogs must learn to distinguish fresh human scents from aged ones, and separate overlapping human scent trails. Additionally, they practice ignoring distractions such as animal scents, food smells, and other human odors. This discipline ensures SAR dogs maintain utmost focus during critical operations.
Cross-Training in Different Environments
SAR dogs undergo cross-training in varied terrains—mountains, forests, urban areas, and disaster sites. This comprehensive preparation is essential as it enables these dogs to adeptly adapt to the broad range of conditions encountered during real missions. Each environment poses unique challenges, and dogs must be versatile in their tracking skills to navigate these effectively.
Developing Handler-Dog Communication Systems
Effective communication between a handler and their SAR dog is another cornerstone of successful training. Handlers use both verbal and non-verbal cues to guide and understand their dogs.
Search Commands
Handlers provide commands to initiate or halt tracking, direct the dog towards or away from specific areas, and indicate when the scent trail has shifted. This clear communication ensures the dog and handler work in unison, enhancing the efficiency of their search efforts.
Non-Verbal Cues
Non-verbal interactions also play a key role. Handlers often rely on body language and gestures to communicate, which is particularly useful in noisy or chaotic environments where verbal commands might be less effective. Through consistent practice, dogs learn to interpret these signals accurately.
Realistic Training Scenarios
To mimic real-world conditions, SAR dogs participate in realistic training drills and simulations. These exercises replicate scenarios like wilderness searches, urban disaster responses, and tracking in diverse weather conditions. This training helps them:
- Adapt to different scent dispersal patterns influenced by environmental factors.
- Develop resilience and adaptability to unforeseen challenges.
- Acquire stamina necessary for extended search operations.
Training SAR dogs is a labor-intensive process that integrates scent recognition, discrimination, environmental workouts, and handler communication. By honing these skills, SAR dogs become indispensable assets in search and rescue operations, responding effectively to a multitude of scenarios.
Let’s now shift focus from understanding training methods to exploring the real-world applications that demonstrate the true capability and significance of SAR dogs in various situations.
Real-World Applications
The real-world applications of Search-and-Rescue (SAR) dogs are remarkable. These highly skilled canines play critical roles in various challenging scenarios, making them invaluable assets in efforts to save lives and bring closure to families. Let’s explore some of the key applications of SAR dogs.
Missing Persons and Wilderness Rescues
One of the most common and essential roles of SAR dogs is finding missing persons. When a hiker is lost in the wilderness or a child goes missing in a public park, time is of the essence. SAR dogs can be deployed quickly, often within hours of the initial report, to begin tracking the lost individual.
Using their powerful sense of smell, SAR dogs can detect the specific human scent left behind by the missing person. Their ability to differentiate complex odor profiles allows them to follow the unique trail of the individual, even in areas filled with various scents. This is particularly important in wilderness rescues, where terrain can be rugged, and scent trails may be challenging to follow.
Disaster Response and Urban Search Operations
SAR dogs are also trained for disaster response, where they are often deployed in the aftermath of natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and landslides. In such scenarios, the agility and olfactory abilities of these dogs are crucial.
They are trained in air-scenting techniques which enable them to detect the scent of survivors trapped under rubble or debris. These dogs can cover large areas quickly, helping rescuers identify locations where people may be buried and increasing the chances of finding survivors in the critical hours following a disaster.
Military and Law Enforcement Tracking Applications
SAR dogs have proven to be effective in military operations and law enforcement as well. In the military, these dogs can track escaped prisoners, locate missing soldiers, and even detect explosives. Their adaptability to various environments, from deserts to jungles, makes them versatile assets in military operations.
Similarly, in law enforcement, SAR dogs assist in tracking down suspects, finding missing evidence, and locating human remains. Forensic tracking by cadaver dogs, who are specially trained to detect the scent of decomposing human tissue, is an essential part of criminal investigations. They help provide critical evidence that can lead to the resolution of cold cases and bring justice to victims.
As we continue to explore the incredible capabilities of SAR dogs, it’s clear that their contributions are extensive and varied. Their applications in real-world scenarios highlight not only their training and skills but also the dedication of their handlers who work alongside them in often perilous conditions. These partnerships are a testament to the bond between humans and dogs, working together to achieve extraordinary outcomes.
Future Innovations in SAR Technology
Search and Rescue (SAR) technology has come a long way, but future advancements promise to elevate the efficiency and effectiveness of SAR operations. Enhancements in wearable devices, artificial intelligence (AI), and drone technology are likely to revolutionize how SAR dogs execute their critical missions.
Integration of Wearable GPS Devices
One of the most promising advancements is the integration of wearable GPS devices for SAR dogs. These devices enable real-time tracking of a dog’s location and movements during search operations. This enhances coordination among search teams, offering critical insights into the areas covered, which helps in strategizing further search efforts.
Wearable GPS devices provide:
- Real-time positioning, crucial for guiding handlers and rescuers.
- Data on the dog’s path, helping to identify areas requiring additional search.
- Enhanced safety for both the dogs and their handlers by preventing them from straying into dangerous zones.
Technological advancements in these devices continue to improve battery life, accuracy, and durability, ensuring they can withstand harsh search environments.
AI-Driven Scent Analysis Systems
Artificial intelligence (AI) holds the potential to transform scent tracking by SAR dogs. AI-driven scent analysis systems can process and interpret intricate patterns in odor data, drawing on vast datasets to predict scent trails and optimize search strategies.
AI can enhance SAR operations by:
- Analyzing environmental data, such as weather and terrain, to predict scent dispersion patterns.
- Providing real-time adjustments to search tactics based on dynamic scent and environmental conditions.
- Assisting handlers in interpreting their dog’s behavior and identifying scent concentration zones.
This innovative application of AI can double down on the incredible natural abilities of SAR dogs, ensuring more precise and efficient search missions.
Drone Technology Complementing Canine Tracking Capabilities
Drones are rapidly becoming indispensable allies in SAR missions. When incorporated with canine tracking, drones can provide comprehensive surveillance and remote sensing, particularly in challenging terrains where human access is limited or slow.
Drones can assist SAR efforts by:
- Covering large areas quickly, providing aerial assessments that can guide ground teams.
- Using thermal imaging to detect heat signatures from missing persons, even in difficult conditions.
- Relaying real-time video feeds, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making.
By providing valuable aerial perspectives and detecting hidden clues invisible from the ground, drones can greatly augment the dogs’ tracking abilities, ensuring faster and safer rescues.
These cutting-edge technologies promise to elevate the efficiency of SAR dogs and their handlers, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in search and rescue missions. As innovation continues, our ability to find and rescue those in need will only grow stronger.









