Introduction: The Emotional Bond Between Humans and Dogs
Humans and dogs share a unique emotional bond that has evolved over thousands of years. This connection extends beyond simple companionship, providing a profound, mutual understanding that enriches lives on both ends of the leash. Dogs are not just pets; they become integral members of our families, offering unconditional love, loyalty, and a remarkable capacity to perceive and react to our emotions.
Why Understanding Canine Emotional Intelligence Matters
Recognizing and understanding canine emotional intelligence is crucial for a harmonious and fulfilling relationship with our furry friends. Dogs’ ability to detect and respond to human emotions can significantly impact their overall well-being and behavior. For instance, dogs that are attuned to their owners’ emotions might offer comfort during times of distress or engage in playful activities when sensing happiness. This mutual emotional connection forms the cornerstone of a deeper interaction that allows for better communication and trust.
Exploring how dogs process emotions can help us understand their needs and behaviors more accurately. It can also enhance training practices by aligning them with the dog’s emotional state, thus fostering a more positive and responsive relationship. Furthermore, understanding canine emotional intelligence is particularly beneficial in identifying dogs suitable for therapy and service roles, where their sensitivity to human emotions is paramount.
How Dogs Recognize and Respond to Human Emotions
Dogs utilize a multi-sensory approach to decode human emotions. They read visual cues such as facial expressions and body language to detect happiness, anger, or fear. For example, a dog may notice a smile and associate it with a positive interaction, while an angry face might prompt a cautious or submissive response.
Auditorily, dogs are highly responsive to vocal tones and emotional sounds. A calm, soothing voice can relax a dog, whereas a loud, angry shout might cause anxiety or fear. They also pick up on olfactory signals through scent changes, which can reflect human emotions like stress, joy, or sadness. For instance, a stressed person may emit a different scent that dogs can detect, prompting them to offer comfort.
The comprehensive ability of dogs to recognize and respond to human emotions highlights the depth of their emotional intelligence and the strong bond they share with humans. This understanding sets the stage for exploring the science behind their emotional recognition capabilities and their practical applications in enhancing human-canine interactions and fulfilling specific roles such as therapy and service work.
The Science Behind Canine Emotional Recognition
Differentiating Human Emotions
Extensive research demonstrates that dogs have an exceptional ability to recognize and differentiate between various human emotions. For instance, studies reveal that dogs can distinguish between happy, angry, sad, and fearful faces using visual cues like facial expressions. They can also detect emotional valence through tone of voice. This sensitivity enables dogs to respond appropriately to their human companions, fostering a deep bond.
Evolutionary Basis
This remarkable emotional sensitivity is rooted in the evolutionary history of dogs. As dogs and humans have co-evolved over thousands of years, dogs have developed heightened emotional perceptiveness to better coexist with humans. Initially, domestication selected for traits that favored cooperation and understanding between humans and dogs. Over time, this has led to an evolved ability to read and respond to human emotions adeptly.
Key Brain Regions
The canine brain plays a crucial role in processing social and emotional cues. Key regions involved include the amygdala and the temporal cortex. The amygdala is central to emotion processing and is activated when dogs encounter emotional stimuli. The temporal cortex helps in integrating sensory information, allowing dogs to form a holistic understanding of human emotions.
Conclusion
Understanding these scientific insights into how dogs recognize and respond to human emotions emphasizes the special bond we share with our canine friends. By appreciating this connection, we can better support our dogs in everyday interactions and enhance our mutual emotional well-being.
How Dogs Perceive Human Emotions: A Multi-Sensory Approach
Dogs have a remarkable ability to perceive human emotions using a combination of visual, auditory, and olfactory cues. This multi-sensory approach allows them to interpret complex emotional states and respond appropriately, strengthening the bond between humans and their canine companions.
Visual Cues: Reading Facial Expressions and Body Language
Dogs are adept at reading human facial expressions and body language. Research has shown that dogs can distinguish between happy, angry, sad, fearful, and neutral faces. They use these visual cues to assess the emotional state of their human companions, often reacting in ways that demonstrate empathy and understanding.
For instance, a dog may approach a person with a relaxed and wagging tail when they see a smiling face, indicating happiness. Conversely, a dog might lower its head or avert its gaze when confronted with an angry or stern expression, showing an understanding of the associated negative emotions.
Auditory Cues: Sensitivity to Vocal Tone and Emotional Sounds
Dogs are highly sensitive to the tone and pitch of human voices. They can discern emotional states from vocal cues, such as the difference between a cheerful, high-pitched voice and a harsh, low-pitched one. This ability allows dogs to respond appropriately to different emotional contexts, offering comfort to distressed owners or joining in the excitement of a joyful moment.
Olfactory Perception: Detecting Emotions Through Scent Changes
Dogs possess an incredible sense of smell, which they use to detect subtle changes in human body odor that correspond to various emotions. Studies suggest that dogs can identify scents associated with fear, stress, and happiness, among other emotions. This olfactory sensitivity enables dogs to provide comfort and support in times of distress, as they can sense their owner’s emotional state even without visual or auditory cues.
Bringing It All Together: Integrating Sensory Information
By combining visual, auditory, and olfactory cues, dogs form a holistic understanding of human emotions. This ability to integrate information across multiple sensory channels allows dogs to accurately assess and respond to their owner’s emotional needs. Understanding this aspect of canine emotional intelligence can help strengthen the human-dog bond and improve interactions in various contexts, from daily life to therapy and service work.
Recognizing how dogs perceive human emotions through a multi-sensory approach highlights the depth of their emotional intelligence. This understanding sets the stage for exploring how dogs’ behavioral responses are shaped by their perception of human emotions.
heartbeats and tail wags
Dogs don’t just see us—they feel us. With their incredible ability to read facial expressions, vocal tones, and even our scent, they tune in to our emotional world like few creatures can. Whether we’re beaming with joy or sinking into stress, dogs pick up the signals and mirror our mood with heart-melting precision.



Understanding this emotional intelligence isn’t just fascinating—it’s essential. It deepens our bond, improves training success, and makes dogs perfect partners in therapy and daily life. These furry companions aren’t just reacting—they’re emotionally connecting.
Cross-Modal Integration: Dogs’ Holistic Understanding
Understanding how dogs integrate visual, auditory, and olfactory information is fascinating. This cross-modal integration enables dogs to develop a holistic understanding of human emotions, enhancing their empathy and interaction with humans. This section explores how dogs match facial expressions with vocal tones, integrate sensory information, and how research supports their cross-modal abilities.
Matching Facial Expressions with Vocal Tones
Dogs have evolved to be highly attuned to human emotional expressions. They can match angry voices with angry faces and happy voices with happy faces. Studies show that dogs’ ability to associate emotional tones with corresponding facial expressions helps them understand human emotional states more accurately. This skill is a product of their domestication and co-evolution with humans, which has fine-tuned their ability to respond to human emotional cues.
Integrating Sensory Information
Dogs do not rely on a single sense to gauge human emotions. Instead, they integrate input from various sensory channels, such as sight, sound, and scent. This multi-sensory approach allows dogs to form a comprehensive picture of their owner’s emotional state. For example, when you return home from a stressful day, your dog can sense your tension not just from your facial expressions, but also from your voice’s tone and changes in your scent.
Research on Cross-Modal Abilities
Various studies demonstrate the extent to which dogs can integrate sensory information. One pivotal study used eye-tracking technology to observe how dogs focus on human faces and expressions. Another study measured physiological responses, like heart rate variability, to different emotional stimuli, confirming dogs’ ability to distinguish emotional states. Experiments in cross-modal discrimination solidify this understanding, proving that dogs can accurately match auditory and visual emotional cues from humans.
Cross-modal integration is an essential aspect of canine emotional intelligence. Dogs’ ability to combine sensory information provides them with a rich, nuanced understanding of humans. This remarkable skill not only strengthens the human-canine bond but also has practical applications in therapy and service work.
Transition
As we explore the ways in which dogs react to human emotions through various behaviors, we gain a deeper appreciation for their empathetic nature.
Behavioral Responses: How Dogs React to Your Emotions
Typical Behaviors When Dogs Sense Happiness vs. Anger or Fear
Dogs have an incredible ability to perceive and react to human emotions. When they sense happiness, dogs often become more lively and playful. You might notice your dog wagging their tail energetically, jumping around, or seeking your attention more by bringing toys or initiating games. These behaviors reflect their own excitement and joy in response to your positive emotions.
On the other hand, when dogs sense anger or fear, their behaviors change noticeably. If you are angry, your dog may exhibit submissive behaviors like lowering their head, tucking their tail, or avoiding eye contact. These actions are signs of appeasement, as dogs instinctively try to avoid conflict. When they detect fear, dogs might stay close, often exhibiting protective behaviors like barking, growling softly, or maintaining a vigilant posture.
Comforting Behaviors Dogs Display When They Detect Human Distress
Dogs are incredibly attuned to signs of human distress. When they detect that their owner is feeling down, anxious, or stressed, dogs often respond with comforting behaviors. Common actions include:
- Proximity seeking: Dogs may sit or lie close to you, providing a sense of companionship and support.
- Gaze engagement: Keeping eye contact to show empathy and understanding.
- Licking: Gentle licking is a comforting gesture often meant to soothe their owner.
- Nuzzling: Dogs may nuzzle their owner’s hand or face, seeking to offer reassurance and affection.
These behaviors highlight dogs’ role as natural emotional support animals, providing comfort when we need it most.
How Dogs Adjust Their Behavior Based on Their Owner’s Emotional State
Dogs are highly responsive to their owner’s emotional state. When you are calm and relaxed, your dog is likely to mirror this sentiment by exhibiting calm and relaxed behavior themselves. They may lounge near you, showing patience and tranquillity. Conversely, when you are anxious or stressed, dogs may respond by becoming more vigilant and attentive, trying to figure out the best way to provide support or comfort.
This awareness in dogs makes them not only faithful companions but also effective participants in interventions such as therapy or service work. By adjusting their behaviors according to our emotions, dogs help create a balanced environment conducive to mutual emotional well-being.
As we delve deeper into understanding our dogs’ emotional intelligence and responses, we can appreciate the profound bond we share. This insight helps to enhance our interactions and strengthen our connection with these remarkable animals.
Factors That Influence Dogs’ Emotional Perception
Breed Differences in Emotional Sensitivity and Responsiveness
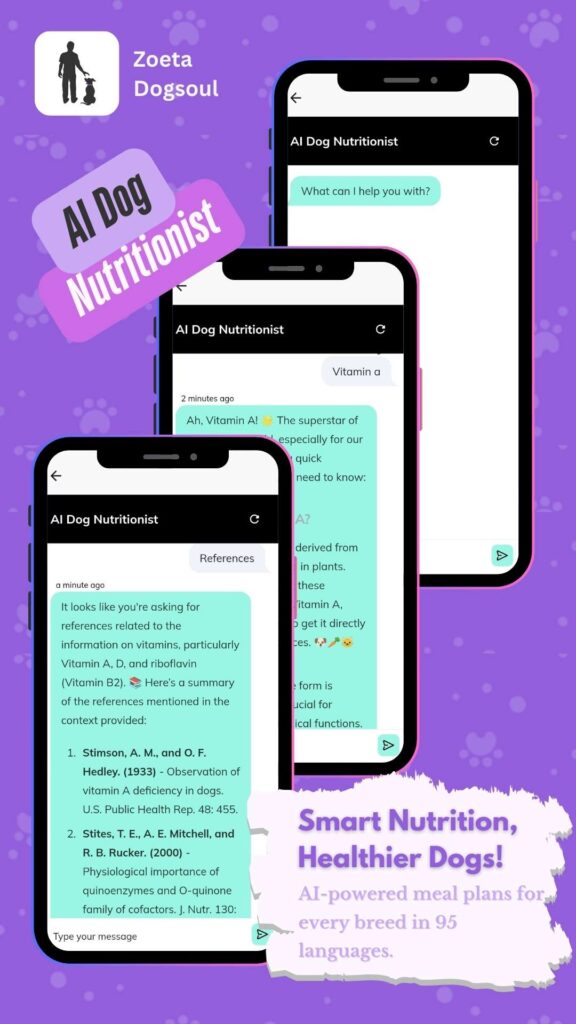
Different dog breeds exhibit varying levels of emotional sensitivity and responsiveness. For instance, companion breeds like Labrador Retrievers and Cavalier King Charles Spaniels are often more attuned to human emotions [A Comprehensive Study on Canine Rec.txt]. These breeds have been selectively bred to be more sociable and responsive to human cues, making them excellent emotional support dogs. On the other hand, working breeds such as German Shepherds and Border Collies, while also sensitive, tend to focus more on tasks and commands. Their training and experience may influence their emotional engagement with humans differently.
The Impact of Early Socialization and Training Experiences
Early socialization and training are crucial in shaping a dog’s ability to perceive human emotions. Puppies exposed to various environments, people, and experiences during their critical socialization period (usually between 3 and 14 weeks) develop better emotional recognition skills [A Comprehensive Study on Canine Rec.txt]. Training that incorporates positive reinforcement also plays a vital role. Dogs that experience positive interactions with humans during their formative months are more likely to develop strong emotional bonds and exhibit higher emotional intelligence.
How the Strength of the Human-Dog Bond Affects Emotional Attunement
The quality and strength of the bond between a dog and its owner significantly impact emotional attunement. Dogs that share a close relationship with their owners are better at reading and responding to their emotional states. This bond is often strengthened through daily interactions, consistent communication, and shared experiences. A strong bond not only improves the dog’s emotional well-being but also enhances their ability to support their owners during emotional highs and lows [A Comprehensive Study on Canine Rec.txt]. Dogs with a secure attachment are more likely to engage in comforting behaviors when they detect their owner is distressed.
These factors highlight the complex interplay between breed, early experiences, and the human-dog bond in shaping a dog’s emotional perception abilities. Understanding these aspects can help in nurturing a deeper, more empathetic connection with our canine companions.
Individual Differences in Canine Emotional Intelligence
Personality Traits Affecting Emotional Perception
Like humans, dogs have unique personality traits that influence their emotional intelligence. Some dogs are naturally more empathetic and attuned to human emotions, whereas others may be more independent and less emotionally reactive. Characteristics such as sociability, curiosity, and nervousness can impact a dog’s ability to perceive and respond to human emotions. For example, a sociable dog may exhibit more comforting behaviors when sensing distress, while an anxious dog might react with heightened sensitivity to any changes in their owner’s emotional state.
Variability in Emotional Sensitivity
The emotional intelligence of dogs varies not only among breeds but also between individual dogs. Research indicates that companion breeds, such as Labrador Retrievers and Golden Retrievers, often display higher emotional sensitivity due to their strong bonds with humans. On the other hand, working breeds, like German Shepherds and Border Collies, might focus more on tasks and less on emotional cues. This variability means that some dogs may excel in therapy and support roles, driven by their intuitive understanding of human emotions, while others perform better in roles requiring task-oriented focus.
Manifestation of Canine Emotional Intelligence
Canine emotional intelligence manifests in various ways, including behavioral responses and their ability to interpret human cues. An emotionally intelligent dog might show empathy by staying close to a sad owner or attempting to cheer up a stressed individual with playful antics. These behaviors stem from their ability to perceive and react appropriately to human emotional states. This intelligence is not just about recognizing emotions but also about responding in ways that strengthen the human-dog bond and provide comfort and support.
By appreciating the uniqueness of each dog’s emotional intelligence, owners can better understand and nurture their canine companions, fostering a deeper connection based on mutual emotional understanding.
Practical Applications: Therapy and Service Work
Why Emotionally Perceptive Dogs Excel
Emotionally perceptive dogs have a natural ability to recognize and respond to human emotions, making them ideal candidates for therapy and emotional support roles. These dogs provide comfort, solace, and stability to individuals experiencing psychological challenges. The strong emotional bond that develops between these dogs and their handlers often leads to significant improvements in mental health and overall well-being.
Understanding Canine Emotional Intelligence in Selection Processes
Selecting the right dogs for therapy and service work requires a deep understanding of canine emotional intelligence. Dogs with high emotional perception are better suited to roles that demand empathy and responsiveness. Trainers and organizations often focus on:
- Breed Selection: Certain breeds, like Labrador Retrievers and Golden Retrievers, are renowned for their gentle temperament and high emotional sensitivity. These breeds often excel in therapy settings due to their innate ability to connect emotionally with humans.
- Behavioral Assessment: Potential therapy dogs undergo rigorous evaluations to determine their ability to handle emotional stress and respond appropriately to human emotions.
- Early Socialization and Training: Dogs that experience early positive socialization and training in diverse environments are more adaptable and empathetic. These experiences enhance their capacity to serve as effective emotional support animals.
Real-World Examples of Canine Emotional Support
Dogs exhibit remarkable behavior when responding to human emotional needs. Some inspiring real-world examples include:
- Hospitals and Nursing Homes: Therapy dogs bring comfort to patients and residents. Their presence lowers stress levels, mitigates feelings of loneliness, and promotes faster recovery.
- Schools: Emotional support dogs in educational settings help reduce anxiety and improve focus among students. These dogs assist in creating a calming atmosphere conducive to learning.
- Disaster Areas: Service dogs are deployed in crisis situations to provide emotional relief to victims and first responders. Their calming influence helps individuals cope with trauma and distress.
Recognizing the multifaceted roles these dogs play in supporting human emotional health is essential. Their unique ability to sense and respond to emotions allows them to perform their duties effectively, strengthening the human-animal bond and enhancing quality of life.
By appreciating these applications, we realize the depth of dogs’ emotional intelligence and their potential to support us in challenging times. This mutual understanding enriches interactions and promotes emotional well-being for both dogs and humans.
Improving Communication With Your Dog
Tips for Being Mindful of Your Emotional Signals Around Your Dog
Dogs possess an incredible ability to sense our emotional states. To make the most of this connection, it’s important to be mindful of the signals you send. Here are some practical tips to enhance communication with your furry friend:
- Consistency Is Key: Dogs thrive on routine and consistency. Consistent emotional signals help them understand your mood and respond appropriately.
- Stay Calm and Positive: Your dog can detect stress or anxiety. Take deep breaths and maintain a calm demeanor to avoid transferring negative emotions.
- Body Language Matters: Be conscious of your posture and facial expressions. Positive body language can reassure your dog and strengthen your bond.
- Use a Gentle Tone: Dogs are sensitive to vocal cues. A gentle and encouraging tone can make a big difference in how your dog perceives your emotions.
How to Strengthen Emotional Bonds Through Consistent Communication
Building a lasting emotional bond with your dog involves more than just being mindful of your signals. Consistent communication is essential. Here’s how you can achieve this:
- Spend Quality Time Together: Regular interaction helps your dog feel secure and loved. Whether it’s playtime, training, or simply chilling on the couch, your presence matters.
- Daily Routines: Establishing daily routines, like regular walks and feeding times, creates a sense of stability and trust.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog’s positive actions and behaviors. Consistent praise and treats reinforce the emotional bond.
- Interactive Play: Engaging in play that involves both physical and mental stimulation can strengthen your relationship and understanding.
Techniques to Help Emotionally Sensitive Dogs in Stressful Situations
Some dogs are particularly sensitive and can easily become stressed. Here are techniques to support your emotionally sensitive dog:
- Create a Safe Space: Designate a quiet, comfortable area where your dog can retreat when feeling overwhelmed.
- Gradual Exposure: Slowly introduce your dog to potentially stressful situations to build their confidence.
- Calming Exercises: Engage in calming activities such as gentle pet massage or aroma therapy. Keep their environment soothing.
- Professional Support: Consult a professional dog trainer or behaviorist if your dog’s stress levels are consistently high. They can provide tailored strategies.
Understanding and improving communication with your dog enhances the mutual emotional well-being. By being mindful, consistent, and supportive, you can foster a profound and rewarding connection.
Training Implications: Emotions Matter
Why Your Emotional State Affects Training Outcomes
When training your dog, your emotional state plays a pivotal role in the success and effectiveness of each session. Dogs are incredibly perceptive to human emotions, often mirroring or reacting to the feelings they sense from their owners. If you’re feeling stressed or frustrated during training, your dog can pick up on these emotions and may become anxious or reluctant to participate. On the other hand, if you maintain a calm and positive demeanor, your dog is likely to respond enthusiastically and be more motivated to learn.
How to Create Positive Emotional Associations During Training Sessions
Creating a positive atmosphere during training is essential for fostering strong learning and emotional connections. Here are some tips to ensure your training sessions are effective and enjoyable:
- Stay Calm and Positive: Keep a calm tone and use positive body language. Dogs respond well to encouragement and praise, so smile and use gentle gestures.
- Consistency is Key: Be consistent with commands and rewards. This helps your dog understand what you expect and reduces confusion.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog immediately when he performs a desired behavior. Treats, verbal praise, and petting are effective rewards.
- Short and Sweet Sessions: Keep training sessions short to maintain your dog’s interest without causing fatigue. Aim for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- End on a High Note: Always conclude training with a successful command and positive reinforcement. This leaves your dog with a positive impression of the session.
Avoiding Emotional Miscommunication When Working With Your Dog
Miscommunication can occur if your dog misinterprets your emotional signals, leading to frustration for both of you. Here’s how to avoid it:
- Be Mindful of Body Language: Dogs are adept at reading non-verbal cues. Avoid sudden or aggressive movements and maintain open physical gestures.
- Clear Vocal Commands: Use clear, distinct vocal commands without emotional undertones that can confuse your dog. Practice using a firm but kind tone.
- Practice Patience: If your dog doesn’t get a command right away, stay patient and avoid showing frustration. Dogs need time to learn and understand.
- Establish Routine: Regular routines provide stability, helping dogs feel more secure and confident. Consistent schedules for training and feeding are beneficial.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you encounter persistent communication issues, consider consulting a professional trainer who can provide tailored advice and strategies.
Understanding the emotional dynamics in your training practice not only improves outcomes but also strengthens the bond with your canine companion. Engaging positively and patiently with your dog ensures a rewarding and harmonious training experience.
By fostering an emotionally supportive environment, you enable better learning and a healthier relationship with your dog.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Current Debates: Do Dogs Truly Understand Emotions or Respond to Conditioned Signals?
The question of whether dogs genuinely understand human emotions or simply react to conditioned signals remains a topic of debate among researchers. On one side, evidence suggests that dogs possess a remarkable ability to recognize and differentiate human emotions using multi-sensory cues. Dogs can interpret facial expressions, vocal tones, and even scents to form a holistic understanding of their owners’ emotional states. However, some experts argue that this behavior may be a result of conditioned responses rather than an innate understanding of emotions.
One perspective is that dogs might not fully grasp the complexity of human emotions but instead rely on associative learning. For instance, if a dog has repeatedly received comfort and affection when its owner is happy, it might learn to approach happy individuals seeking positive interactions. Conversely, dogs may avoid angry or fearful humans due to previous negative experiences. While this shows a high level of perceptual prowess, it raises questions about the depth of their emotional understanding.
Promising Areas for Future Research in Canine Emotional Perception
Many exciting avenues exist for future research in understanding canine emotional perception. One significant area needing exploration is whether dogs can comprehend the intentions behind human emotions. Understanding not just the emotional state but also the underlying intent could provide deeper insights into canine empathy and cognition.
Another promising field is investigating the influence of environmental contexts on dogs’ emotional recognition. Various factors, such as different social settings, the presence of familiar versus unfamiliar individuals, and the dynamics of human-dog interactions, could significantly impact how dogs perceive and respond to emotions.
Critical research tools, such as eye-tracking studies, heart rate variability measurements, and cortisol analysis, could be employed to understand better how dogs process emotional cues. Additionally, experiments comparing dogs’ responses to synchronous visual and auditory emotional signals could shed light on their cross-modal sensory integration abilities.
How Longitudinal Studies Might Track Emotional Development from Puppyhood to Adulthood
To gain a comprehensive understanding of emotional development in dogs, longitudinal studies are essential. These studies follow dogs from puppyhood through adulthood, providing valuable insights into how their emotional perception evolves over time. Longitudinal research could examine how early experiences, socialization, and training influence the ongoing development of emotional intelligence in dogs.
Such studies would help identify critical periods during which dogs are most receptive to learning about human emotions. Understanding these sensitive phases could inform breeding practices, socialization techniques, and training methods that optimize dogs’ emotional perception and responsiveness.
By recognizing the factors that contribute to the development of emotional intelligence in dogs, owners and trainers can better support and nurture these abilities. This, in turn, enhances the bond between humans and dogs, ensuring more effective communication and emotional attunement between species.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Emotional Intelligence of Dogs
Summary of Key Insights
Dogs have demonstrated a remarkable ability to recognize and respond to a variety of human emotions. Research has consistently shown that dogs can differentiate between expressions of happiness, anger, sadness, and fear across multiple sensory channels such as visual cues, vocal tones, and changes in scent. Key brain regions, particularly the amygdala and temporal cortex, play a significant role in processing these emotional signals, which underscores the complexity of canine emotional intelligence.
Mutual Benefits of Emotional Attunement
The emotional bond between humans and dogs offers profound mutual benefits. For humans, the companionship of a dog can provide emotional support, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Dogs, with their keen sensitivity to human emotions, often exhibit comforting behaviors such as proximity seeking, gaze engagement, and physical touch when their owners are in distress. This empathetic reaction not only helps humans cope with negative emotions but also strengthens the bond between the two.
In roles such as therapy and service work, emotionally perceptive dogs alleviate anxiety, provide comfort, and enhance the emotional recovery for individuals in various settings, including hospitals and disaster areas. Understanding and nurturing a dog’s emotional intelligence can lead to more effective therapeutic interactions and a deeper, more harmonious human-dog relationship.
Encouragement to Appreciate and Nurture Your Dog’s Emotional Intelligence
It is essential to appreciate and actively nurture your dog’s emotional intelligence. Engaging in consistent communication, positive reinforcement, and mindful emotional signaling can reinforce your dog’s ability to perceive and respond to your emotions accurately. Spending quality time, creating a safe and comforting environment, and training with an awareness of your emotional state further foster their emotional growth.
By recognizing the depth of their emotional intelligence, we can celebrate our dogs not only as loyal companions but as empathetic participants in our emotional lives. This appreciation enriches both our lives and theirs, forging a connection that is both profound and enduring.









