Why Understanding Canine Body Language Matters
Dogs are fascinating creatures with their own unique mode of communication. Unlike humans, they primarily utilize body language to convey their feelings, intentions, and needs. This distinctive mode of communication makes it imperative for dog owners to develop a keen understanding of canine body language. Misinterpreting these signals can lead to stress, aggression, or fear in dogs, whereas proper comprehension can significantly enhance the human-dog bond.
Dogs Communicate Primarily Through Body Language
Dogs, much like humans, have a rich tapestry of expressions and gestures that communicate their inner world. However, instead of relying heavily on vocalizations, dogs use physical signals to express themselves. This reliance on body language means that a lot of what dogs are feeling or planning can be observed through their posture, tail movement, facial expressions, and other physical indicators.
- Facial cues and head positions: A dog’s eyes, ears, and mouth can tell you a lot about how they are feeling. Soft eyes usually indicate relaxation and friendliness, while a hard stare can be a warning sign or display of discomfort. Similarly, the positioning of their ears—whether they are pinned back, relaxed, or erect—offers clues about their emotional state.
- Tail language: Various tail positions carry different meanings. A high, confident wagging tail often signals excitement or alertness, whereas a low, tucked tail suggests fear or submission.
Misinterpreting Signals Can Lead to Stress, Aggression, or Fear
Failure to accurately interpret a dog’s body language can have adverse effects. For example, assuming that a wagging tail always means happiness can be misleading. Dogs can wag their tails out of nervousness or even aggression, depending on the situation and tail movement patterns.
Misunderstanding these cues can result in:
- Stress: Dogs may feel uneasy or anxious if their signals for needing space or feeling threatened are ignored. This can escalate to more problematic behaviors.
- Aggression: Ignoring warning signs, such as a stiffened body or a hard stare, can provoke aggression. Dogs may feel they need to protect themselves when their subtle indications of discomfort are unnoticed.
- Fear and retreat: When dogs sense that their signals for fear or submission, like crouching or rolling over, are not understood, they can become more fearful and less confident.
Proper Understanding Strengthens the Human-Dog Bond
Recognizing and appropriately responding to your dog’s body language is essential for a healthy and strong relationship. Acknowledging a dog’s cues helps to build trust and reduce behavioral issues:
- Trust building: When dogs see that their owners can read and respect their body language, they feel more secure and confident. This trust is pivotal in ensuring a happy, calm, and obedient pet.
- Reduction of behavioral problems: Understanding the nuances of canine communication allows for early intervention in potentially problematic scenarios, reducing the likelihood of aggression or stress-related behaviors.
- Enhanced bonding: Properly interpreting and reacting to a dog’s needs fosters a deeper emotional connection. Owners who ‘listen’ to their dogs through body language tend to have more aware and responsive pets.
To interact successfully with dogs, it’s essential to look beyond the surface level cues and consider the overall physical signals, environment, and context. By developing this understanding, you can ensure a harmonious and respectful relationship with your furry friend.
Learning to read your dog’s body language effectively is a continuous process, yet the rewards of a strong, trust-filled bond are immense. Understanding these cues will empower you to meet your dog’s needs better and enjoy a more fulfilling companionship.✌️
Facial Expressions and Head Positions
Reading your dog’s facial expressions and head positions can offer deep insights into their feelings and intentions. Let’s delve into some key aspects of canine body language focusing on these areas.
Eye Contact: Soft Eyes vs. Hard Stare
Eyes are a window to the soul, and this holds true for dogs as well.
- Soft Eyes: When your dog has soft, relaxed eyes, it’s a sign they are comfortable and friendly. Such expressions indicate trust and contentment.
- Hard Stare: A hard, unblinking stare can signify discomfort, tension, or a warning. Dogs use this intense gaze to signal that they want to be left alone or they may be feeling threatened.
Avoid direct prolonged eye contact as it can be perceived as a challenge or a threat.
Ear Positions: Forward, Pinned-Back, and Relaxed
Ears are excellent indicators of a dog’s emotional state. Different positions can reveal a lot:
- Forward Ears: Erect and forward-leaning ears show that a dog is alert and interested in what’s happening around them. This could range from curiosity to anticipation.
- Pinned-Back Ears: When a dog pins their ears back against their head, it often means fear or submission. It can also indicate anxiety or discomfort.
- Relaxed Ears: Ears that are in their natural, relaxed position indicate calmness and that the dog is comfortable in their environment.
Observing ear positions along with other cues can help you gauge your dog’s emotional state more accurately.
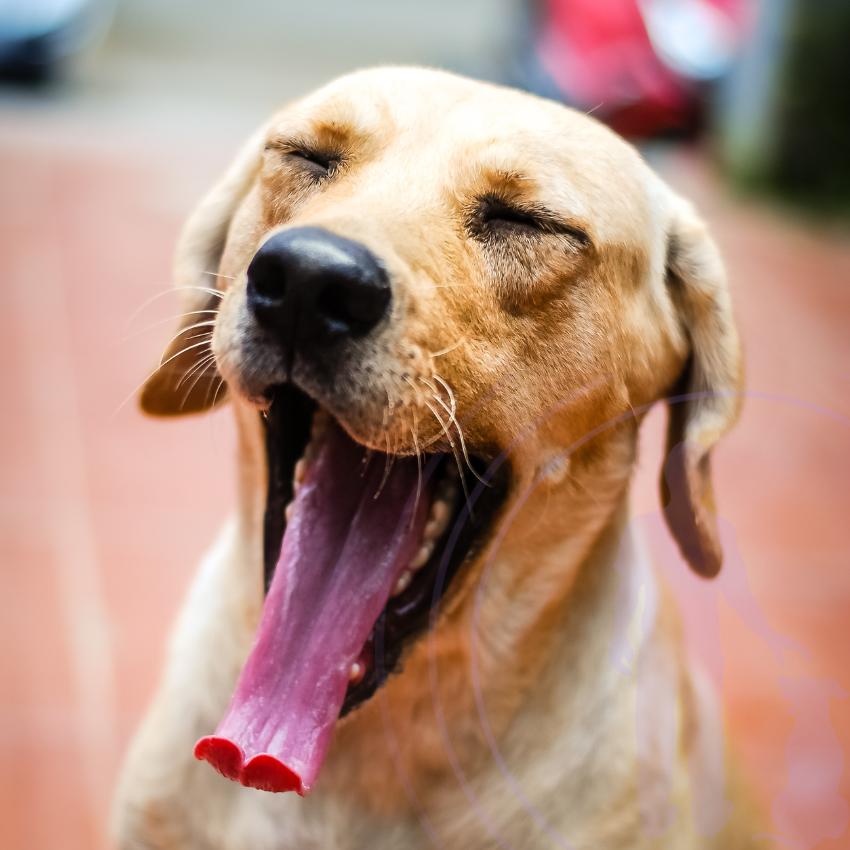

Mouth Signals: Relaxed Open Mouth vs. Stress Signals
The mouth and lips can tell a lot about how a dog is feeling:
- Relaxed Open Mouth: A slightly open mouth with a lolling tongue often shows that a dog is happy and relaxed. This is a good sign that your dog is at ease.
- Lip Licking: Lip licking can often be missed, but it’s a subtle sign of stress or anxiety. If you notice this, it’s an indication that your dog might be uncomfortable or nervous.
- Yawning: Contrary to popular belief, yawning is not always a sign of tiredness. In dogs, it is more often a calming signal or a sign of stress or stress release.
Understanding these signals and observing them in context can help you address your dog’s needs better.
The way your dog’s eyes, ears, and mouth express their feelings is remarkable. By paying closer attention, you can navigate their emotional landscape more effectively. Up next, we’ll explore how tail communication plays a vital role in understanding what your dog is trying to convey.
Understanding Tail Communication
Different Tail Positions and What They Indicate
Your dog’s tail is like a barometer, constantly signaling its emotions and intentions. Understanding these tail positions can significantly enhance your bond with your furry friend. Let’s break down a few common tail positions and what they typically communicate:
- High Tail Position: When a dog holds its tail high, it usually indicates excitement or alertness. This position suggests the dog is confident and attentive to its surroundings.
- Low Tail Position: A tail held low often signifies submission or relaxation. It can also mean the dog is feeling unsure and is adopting a less dominant stance.
- Tucked Tail: A tail tucked between the legs is a classic indication of fear or submission. This posture is often seen in situations where the dog feels threatened or anxious.
By regularly observing your dog’s tail position, you can get a good sense of their emotional state and respond accordingly.
Why a Wagging Tail Doesn’t Always Mean Happiness
A wagging tail doesn’t always equate to a happy dog. Indeed, the context and manner of the wagging are crucial in interpreting its true meaning.
- Gentle Wagging: A gentle wag with a relaxed body generally indicates friendliness and a comfortable state of mind.
- Rapid and Stiff Wagging: Conversely, a tail wagging rapidly with a stiff posture might signal nervousness, excitement, or even aggression. It’s essential to pay attention to the accompanying body language to accurately gauge the situation.
By distinguishing between different types of wagging, you can better understand your dog’s feelings at any moment.
How to Read Tail Movement Patterns
Tail movement patterns can provide additional nuances, enriching your understanding of canine communication:
- Gentle Wagging: As previously noted, gentle wagging, especially when the tail is at a mid-level, often indicates a relaxed and friendly dog.
- Rapid Wagging: Rapid wagging can signal high energy or excitement. It’s often paired with other signals like jumping or spinning, which denote a playful mood.
- Stiff Wagging: Stiff wagging accompanied by a tense body can indicate that the dog is on high alert, potentially feeling threatened or aggressive.
Understanding these subtleties helps in accurately interpreting your dog’s emotional landscape, enabling better and safer interactions.
By carefully observing and interpreting these tail cues along with other body signals, you can build a richer, more empathetic relationship with your dog. Recognizing that each dog may have slightly different body language based on breed and personal history is essential in your ongoing journey to understand your canine friend. You should always ensure you are looking at the whole picture for a comprehensive interpretation of your dog’s communication.
Next, we will delve into reading the overall body posture of your dog to further enhance your ability to understand their emotional states.
Body Postures and Their Meanings
Play Bow and Its Significance in Dog Communication
One of the most joyful signals a dog can give is the play bow. When a dog lowers its front legs and raises its hindquarters, it’s a clear invitation: “Let’s play!” This posture is more than just a play request; it reassures other dogs and people that the dog means no harm. The play bow is quite an endearing sight, indicating fun and friendliness. It’s essential to recognize this signal to understand that the dog wants to play and not to misinterpret it as any form of aggression or submission.
Stiff vs. Relaxed Body Postures and What They Indicate
Dogs’ body postures are a significant indicator of their emotional state. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Stiff Posture: If a dog stands or sits stiffly, it might be feeling tense, wary, or even aggressive. This posture often accompanies other signs like a hard stare, erect ears, and a wagging tail that is more stiff than usual. It’s a warning to stay cautious and observe carefully for other signals.
- Relaxed Posture: A relaxed dog will display a loose, casual posture. Its movements are free, and its body is not rigid. Other signs include soft eyes, a wagging tail with gentle movements, and a relaxed open mouth. This indicates the dog is calm, content, and comfortable in its surroundings.
Understanding these nuances can be crucial in preventing misunderstandings that can lead to stress or aggressive encounters. By observing these postures, we can respond appropriately to ensure the dogs feel safe and understood.
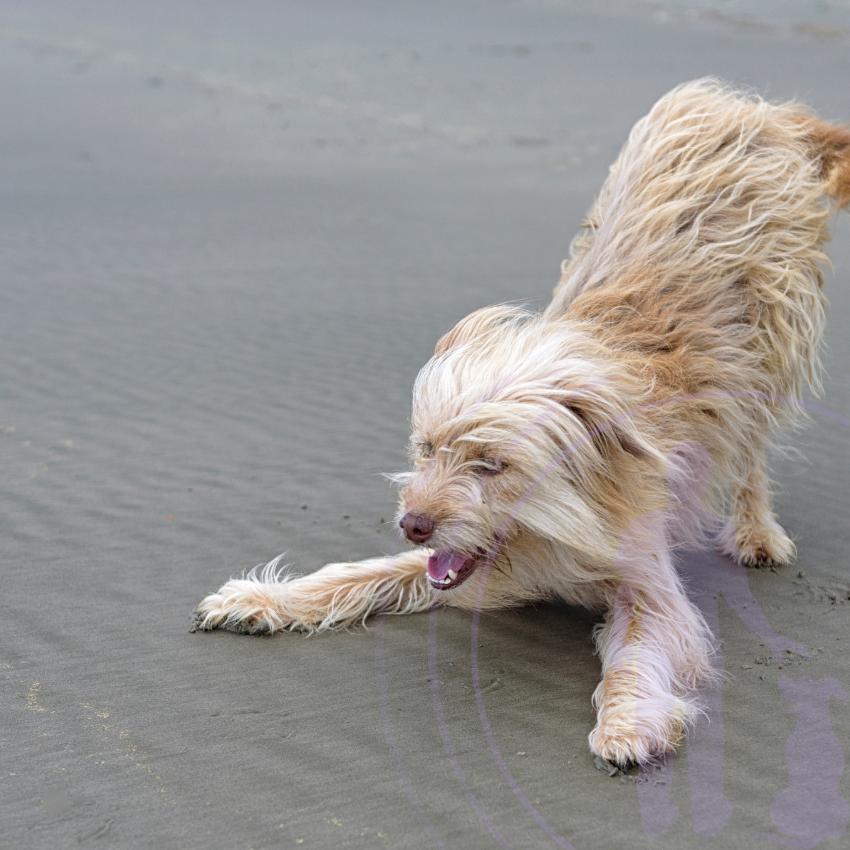

Submissive Positions Including Rolling Over and Crouching
Dogs also display submissive behaviors through their body language, which is vital for peaceful interactions in the canine world. Here are some common submissive positions:
- Rolling Over: When a dog rolls onto its back, it exposes its belly. This gesture is a sign of submission, indicating trust and a desire to avoid conflict. However, context is key—dogs may also roll over as a play signal or to solicit attention and belly rubs.
- Crouching: A dog might lower its body close to the ground, tuck its tail between its legs, and avoid eye contact. This position shows fear or submission, signaling the dog is not a threat and wishes to avoid confrontation. This behavior is more common in anxious or stressed dogs, and recognizing it can help in providing reassurance and comfort.
By paying attention to these body postures and understanding their meanings, you can foster a more positive and secure environment for your dog. Proper interpretation of these signals allows you to respond appropriately, thus ensuring a stronger bond and better communication between you and your canine companion.
As we delve deeper into understanding various canine signals, it’s crucial to remember that context plays an essential role in interpreting these signs.
Context Matters: Reading the Whole Picture
Understanding canine body language requires a holistic approach. Context plays a significant role in interpreting signals accurately. Let’s dive into how the environment and other factors influence a dog’s body language, and the importance of considering multiple signals together.
How Environment Affects Body Language Interpretation
Dogs are highly sensitive to their surroundings, and the same body language cues can mean different things depending on the context. For instance, a dog displaying a wagging tail in a familiar, comfortable environment might be showing happiness and relaxation. However, the same wagging tail in an unfamiliar or stressful environment could indicate nervousness or uncertainty.
Environmental factors to consider include:
- Presence of other dogs or people: The social dynamics at play can influence a dog’s body language. A dog might exhibit submissive behavior around dominant dogs or show excitement when greeting familiar people.
- Prior experiences: A dog’s past, including socialization or trauma, affects its current body language. For example, a dog that has experienced aggression may appear more defensive in new environments.
- Immediate environment: Familiar vs. unfamiliar settings can drastically change a dog’s body language. A dog may display more confident behavior at home but be more cautious or submissive in a new place.
Importance of Considering Multiple Signals Together
Isolated cues can be misleading. It’s essential to observe your dog’s whole body to get an accurate read on its emotions and intentions. Here’s why:
- Eye contact combined with posture: A hard stare alone may seem aggressive, but if paired with a relaxed body, it might simply indicate intense curiosity or focus.
- Tail movement along with ear position: A wagging tail combined with pinned-back ears can signal mixed emotions, such as nervousness or conflicting feelings.
- Mouth signals alongside body posture: A relaxed mouth with gentle panting suggests calmness, but if the body is tense, it could indicate readiness to act aggressively if provoked.
Paying attention to the interplay of these signals helps avoid misunderstandings and fosters a clearer communication channel with your dog.
Breed-Specific Variations in Body Language
Different dog breeds have unique physical traits that can affect their body language. It’s crucial to understand these breed-specific variations to interpret signals accurately [Walsh et al., 2024].
- Huskies: Huskies often howl instead of barking, and their erect ears can denote alertness or friendly engagement depending on the context.
- Greyhounds: Greyhounds may tuck their tails even when they are calm, which can be mistaken for fear or submission.
- Pugs and Bulldogs: Breeds with short muzzles might have facial expressions that appear different from longer-muzzled breeds. For example, panting in these breeds could look more like a grin.
Considering these breed-specific traits ensures that you don’t misinterpret your dog’s body language, leading to better communication and a stronger bond.
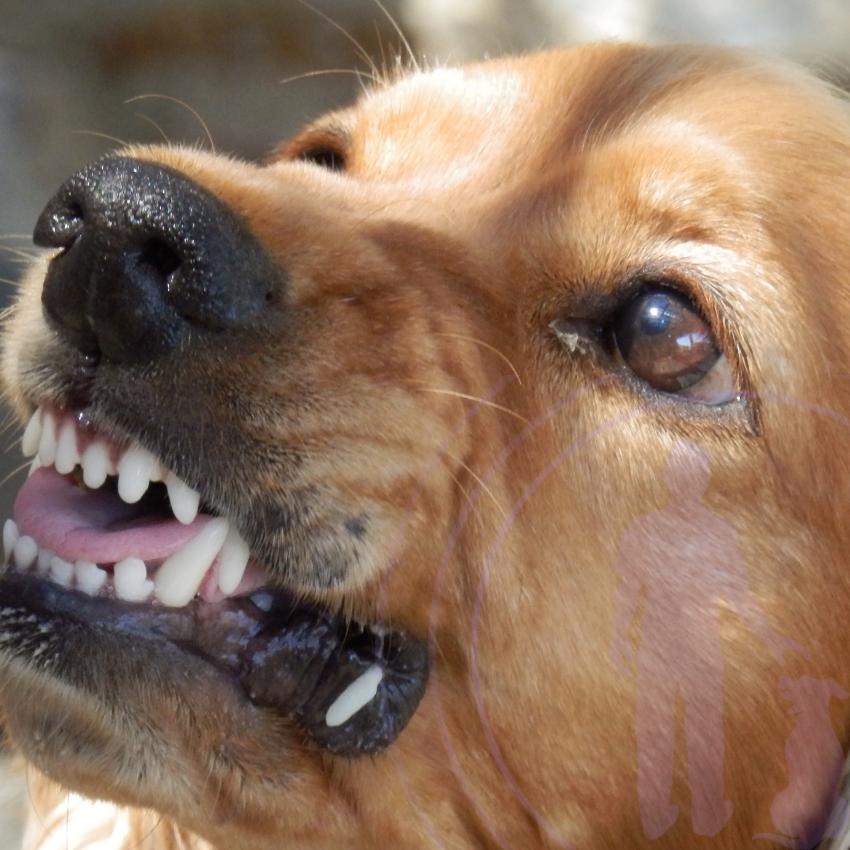

Aggressive Dog Body Language: Recognizing the Signs
Understanding aggressive dog body language is crucial for ensuring safety and maintaining a harmonious relationship with your dog. Aggressive signals can often be subtle, yet they are vital indicators of a dog’s discomfort or potential threat. Recognizing these signs early can prevent escalation and help manage situations effectively. One of the primary indicators of aggression in dogs is a rigid and tense body posture. When a dog feels threatened or is preparing to assert dominance, its body becomes stiff, and it may lean forward in a “ready” stance. This posture is often accompanied by raised hackles, where the fur along the back stands up, signaling heightened alertness or agitation. Additionally, an aggressive dog might display a hard stare, with eyes fixed intently on the perceived threat, conveying a clear warning to back off. Another key aspect of aggressive dog body language is the position and movement of the tail. Contrary to popular belief, a wagging tail does not always signify friendliness. In aggressive contexts, the tail may be held high and move in short, rapid motions, indicating tension rather than joy. Similarly, the ears play a significant role; they may be pinned back against the head or positioned forward, showing the dog’s focus and readiness to react. Understanding these cues allows owners to respond appropriately, ensuring both their safety and that of their canine companion.
By understanding how environment and context influence a dog’s body language, considering multiple signals together, and recognizing breed-specific variations, owners can enhance their ability to interpret and respond to their dogs effectively. This comprehensive view promotes a healthier and more understanding relationship, ultimately improving the overall well-being of both dogs and their owners.
Common Misinterpretations to Avoid
Interpreting your dog’s body language can sometimes be challenging. Misunderstandings and misconceptions are quite common, and can lead to stress and conflict between you and your furry friend. Let’s dive into some of the most prevalent misinterpretations to avoid.
Popular Misconceptions About Tail Wagging and Happiness
One of the most common misunderstandings is the belief that a wagging tail always signifies happiness. While a wagging tail can indicate excitement or friendliness, it can also mean other things.
- High, rapid wagging: This can often signal alertness or agitation, not just joy.
- Low, stiff wagging: This might indicate uncertainty or stress.
- Gentle, relaxed wagging: Generally indicates contentment and friendliness.
It’s important to observe the context and other body signals alongside the tail movement to accurately gauge what your dog is feeling.
Misunderstanding Stress Signals Like Yawning
Another common misinterpretation is assuming that yawning always indicates tiredness. While it can mean your dog is sleepy, it is also frequently a sign of stress or anxiety.
- Frequent yawning: This is often an appeasement gesture or a sign that your dog is feeling stressed.
- Lip licking: Similar to yawning, this can also be a stress signal rather than just a part of grooming.
Recognizing these signals correctly can help you address your dog’s anxiety before it escalates.
How to Avoid Common Interpretation Mistakes
Interpreting canine body language accurately involves considering multiple signals in context. Here are some practical tips to help avoid common mistakes:
- Context matters: Always consider the environment and situation your dog is in. A tail wag in a crowded park might mean something different than at home.
- Look at the whole picture: Combine signals like tail position, ear posture, and facial expressions rather than relying on one cue.
- Know breed-specific quirks: Different breeds may have unique ways of expressing themselves. For instance, Huskies may howl instead of bark, and Greyhounds may tuck their tails even when they are calm.
Understanding these nuances can help you build a stronger, more empathetic bond with your dog.
By recognizing the full range of your dog’s body language and interpreting it within the proper context, you can foster a positive and supportive relationship. Your dog will appreciate your efforts to understand them better, leading to a happier, more harmonious life together.
Practical Tips for Better Communication
Understanding canine body language is more than just interpreting a single wag of the tail or a quick glance. To improve communication with your dog, it’s crucial to observe the entire body and consider the context of their actions. Here are some practical tips to enhance your communication and foster a stronger bond with your furry friend.
Observing the Whole Body Rather than Isolated Signals
Dogs communicate through a combination of body language signals, and interpreting these cues accurately requires observing the whole body.
- Eyes: Soft, relaxed eyes usually indicate calmness, while avoiding eye contact can signal submission or fear. A hard stare may indicate a warning or discomfort.
- Ears: Forward ears show alertness or confidence, pinned-back ears indicate fear or submission, and relaxed ears signify contentment.
- Mouth: A relaxed, open mouth often means the dog is happy or calm. Growling, lip licking, or yawning can indicate stress or fear.
- Tail: Tail position and movement provide key insights. A high, wagging tail can indicate excitement or alertness, while a tucked tail signals submission or fear.
Observing multiple signals together rather than isolating one ensures a more accurate interpretation of your dog’s mood and intentions.
Practicing Patience and Positive Reinforcement
Building trust and effective communication with your dog requires patience and positive reinforcement. Dogs respond well to rewards and gentle encouragement.
- Be Patient: Take time to understand your dog’s cues and be patient as they learn to communicate their needs and emotions. Remember, building a strong bond takes time and consistent effort.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your dog for displaying calm and relaxed behaviors. Treats, praise, and gentle petting can be powerful tools for reinforcing positive behaviors.
- Avoid Punishment: Avoid punishing fearful or stress-based behaviors. Punishment can increase anxiety and hinder effective communication. Instead, offer reassurance and create a safe environment for your dog.
When and How to Respond to Different Body Language Cues
Knowing when and how to respond appropriately to your dog’s body language can prevent misunderstandings and create a harmonious relationship.
- Relaxed and Content: When your dog displays soft eyes, relaxed ears, and a wagging tail, engage with them in a positive manner. Offer praise and spend quality time together.
- Fearful or Anxious: If your dog exhibits signs of fear or anxiety (e.g., tucked tail, pinned-back ears), provide a calm and reassuring presence. Avoid direct eye contact and loud noises, which may increase their stress.
- Aggressive or Defensive: In situations where your dog shows aggression (e.g., a hard stare, growling, stiff body), give them space and avoid confrontations. Redirect their attention to a more positive activity and ensure they feel secure.
By observing the whole body, practicing patience, and responding appropriately to your dog’s body language, you will foster a deeper understanding and create a stronger, more trusting bond. Continue enhancing your ability to read and respond to your dog’s cues to ensure a happy and healthy relationship.
Unravel the Enigma: Speak Your Dog’s Language
So, you’ve unlocked the secrets of your dog’s body language, from the subtle curve of their ears to the silent dance of their tail. You’ve seen how misinterpreting these signals can lead to stress, aggression, or fear, but armed with this knowledge, you’re now equipped to navigate the complex world of canine communication.
Imagine the transformation in your relationship with your four-legged friend as you begin to understand their silent whispers. You’ll anticipate their needs, respect their boundaries, and deepen that unbreakable bond between you both.
Your mission, should you choose to accept it, is to put this newfound education into action. Start with small steps: observe your dog closely, decipher their body language, and respond accordingly. Celebrate the breakthroughs, learn from the missteps, and always, always listen.
Ready to become your dog’s translator? Share your newly gained insights with fellow dog owners, help them decode their pets’ body language, and together, let’s foster a world where dogs and humans communicate beautifully, without words.
Let’s embark on this journey together – after all, every wag, every stare, every tail wiggle, is a story waiting to be understood.









