Understanding Carbohydrates in Canine Nutrition
Dogs, classified as facultative carnivores, have adapted remarkably well to digest and utilize carbohydrates, especially when these are derived from whole food sources. This evolutionary advantage means that while carbohydrates are not essential nutrients for dogs, they still serve significant roles in their diet. This chapter will delve into the three main categories of carbohydrates: sugars, starches, and fibers, and their importance in canine nutrition.
Digestive Evolution of Dogs
Dogs have undergone notable evolutionary changes allowing for effective carbohydrate digestion. Their digestive systems have adapted to break down carbohydrates and use them efficiently. This adaptation is particularly visible in domesticated dogs that rely on commercial dog food, which often contains carbohydrate-rich ingredients. This efficiency is due to the presence of specific enzymes, such as amylase, that break down carbohydrates into simpler sugars that dogs can utilize.
Categories of Carbohydrates
Understanding the types of carbohydrates is crucial to grasping how they benefit our canine companions. Let’s break down the three main categories:
Sugars
Sugars, also known as simple carbohydrates, are fast-digesting molecules that provide quick bursts of energy. Common sources of sugars in a dog’s diet include certain fruits like apples and bananas. While these should be given in moderation due to their high sugar content, they can serve as excellent quick-energy treats.
Starches
Starches are complex carbohydrates that digest more slowly and provide sustained energy over a longer period. Sources of starch include whole grains like brown rice, oats, and barley. These carbohydrates are particularly beneficial for maintaining steady energy levels, making them ideal for dogs requiring extended physical exertion.
Fibers
Dietary fibers are indigestible carbohydrates crucial for digestive health. They aid in maintaining regular bowel movements and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Sources of dietary fiber include vegetables like pumpkin, green beans, and legumes such as peas and lentils.
Importance of Carbohydrates
Despite not being essential, carbohydrates play an integral role in a dog’s diet. Here’s how they contribute:
Primary Energy Source
Carbohydrates are metabolized into glucose, an essential energy source. Dogs, especially active ones, benefit from this steady energy supply which helps power their daily activities and high-energy exercises.
Protein-Sparing Effect
By providing an alternative energy source, carbohydrates allow proteins to be used for other vital functions, such as muscle repair and growth. This protein-sparing effect is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and overall health.
Gut Health and Fiber Benefits
Fiber supports healthy digestion and prevents issues like constipation. It also promotes a healthy gut microbiome, which is vital for overall health and a strong immune system.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Complex carbohydrates help regulate blood sugar levels, which can be particularly beneficial for dogs with diabetes. Choosing low-glycemic carbohydrates, like oats and barley, ensures a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream, helping maintain balanced blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Understanding the critical functions of carbohydrates helps in appreciating their value in providing a balanced and nutritious diet for dogs. As we transition to exploring the different types and sources of carbohydrates, it’s important to recognize that these nutrients significantly boost a dog’s energy levels, support digestive health, and contribute to overall well-being.
Types and Sources of Carbohydrates for Dogs
Understanding the various types and sources of carbohydrates can help you make informed decisions about your dog’s diet. Carbohydrates for dogs can be broadly classified into three categories: simple carbohydrates, complex carbohydrates, and dietary fiber. Each type plays a unique role in ensuring your dog stays healthy and energetic.
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are sugars that provide a quick burst of energy. These are particularly useful for dogs requiring immediate energy, such as during short periods of intense activity. Fruits are excellent sources of simple carbohydrates and can be included in your dog’s diet in moderation.
Examples of Simple Carbohydrates
- Fruits: Apples (without seeds), bananas, blueberries.
- Honey: Small amounts can occasionally be given as a treat.
Simple carbohydrates from fruits are loaded with additional nutrients like vitamins and antioxidants, which can promote overall health and well-being. However, it’s essential to manage portions to avoid excessive sugar intake.
Complex Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates are starches that provide sustained energy. These are digested more slowly than simple carbohydrates, ensuring a steady release of glucose into the bloodstream. Including complex carbohydrates in your dog’s diet can maintain energy levels throughout the day and support overall health.
Examples of Complex Carbohydrates
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oatmeal, quinoa.
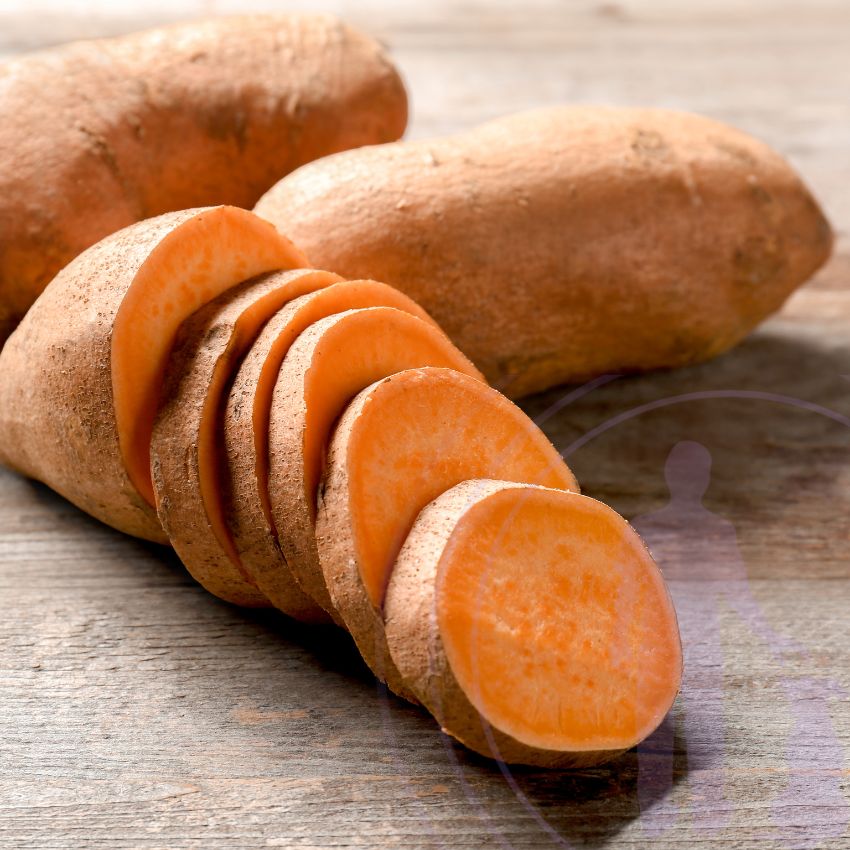
- Vegetables: Sweet potatoes, pumpkin, carrots.
Complex carbohydrates from whole grains and vegetables are also rich in essential nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, and minerals. This makes them a wholesome addition to your dog’s diet, supporting long-term health and well-being.
Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber is crucial for maintaining your dog’s digestive health. It comes in two main forms: soluble and insoluble fiber. Both types of fiber play vital roles in your dog’s gut health by assisting in digestion, promoting regular bowel movements, and supporting beneficial gut bacteria.
Examples of Dietary Fiber
- Vegetables: Pumpkin, green beans, carrots.
- Legumes: Lentils, peas, chickpeas (in limited quantities).
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oatmeal.
Fiber-rich carbohydrates help to regulate digestion and prevent issues like constipation or diarrhea. Moreover, fiber can contribute to weight management by promoting a sense of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Key Points to Remember
- Balance and Moderation: Ensure a balanced intake of different types of carbohydrates to support your dog’s diverse nutritional needs.
- Quality Sources: Opt for whole food sources of carbohydrates rather than refined or processed options.
- Monitoring Intake: Adjust carbohydrate levels based on your dog’s life stage, activity level, and specific health requirements.
This detailed understanding of carbohydrate types and sources will empower you to optimize your dog’s diet effectively. Carbohydrates play a significant role in providing energy, supporting digestion, and maintaining overall health.
As we delve deeper into canine nutrition, it’s important to consider the specific functions and benefits carbohydrates offer to our furry companions.

Key Functions and Benefits
Energy Production and Protein-Sparing Effects
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in your dog’s diet by providing immediate energy. As a primary energy source, carbohydrates are metabolized into glucose, which fuels physical activities. This becomes particularly essential for active dogs, working dogs, and those engaging in high-energy activities.
An added benefit of sufficient carbohydrate intake is its protein-sparing effect. When carbohydrates supply energy, proteins can focus on their main tasks, such as muscle repair and growth. By sparing proteins from being used for energy, carbohydrates help maintain muscle mass and overall health. This protein-sparing effect is beneficial for dogs of all life stages, ensuring that valuable proteins are allocated for their critical functions.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Complex carbohydrates are vital in regulating blood sugar levels. These carbs digest slowly, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar that can lead to problems like energy crashes and insulin resistance. By maintaining steady glucose levels, complex carbohydrates support overall health and can be particularly helpful in managing conditions like diabetes. Foods like sweet potatoes, brown rice, and oats are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates, offering sustained energy release.
Gut Health Maintenance and Immune System Support
Dietary fiber, derived from vegetables, legumes, and whole grains, is indispensable for digestive health. Fiber supports regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This balance is crucial for your dog’s overall gut health, reducing occurrences of diarrhea and other digestive issues.
Moreover, fiber has prebiotic effects that enhance the diversity of the gut microbiome. A diverse gut microbiome is linked to a robust immune system, as a healthy gut can better fend off pathogens and absorb nutrients effectively. Including fiber-rich foods like pumpkin, carrots, and green beans in your dog’s diet can significantly contribute to their digestive and immune health.
By understanding the critical functions and benefits of carbohydrates, especially in terms of energy production, blood sugar regulation, and gut health maintenance, you can make informed decisions about your dog’s diet. Ensuring an appropriate balance of carbohydrates can lead to a healthier, more active, and happier dog.
Nutritional Guidelines and Requirements
When it comes to your dog’s diet, understanding the proper nutritional requirements is crucial. Carbohydrates, while not essentially required, play a significant role in many commercial dog foods. Let’s dive into what makes this nutrient vital at various stages of your canine’s life.
Carbohydrate Content in Commercial Dog Foods
Typically, commercial dog foods contain about 30-60% carbohydrates on a dry matter basis. These carbohydrates come from a mix of grains, vegetables, fruits, and legumes. This broad range accommodates the diverse dietary needs of dogs based on their age, size, activity level, and health conditions.

Carbohydrate Requirements by Life Stage
Puppies
Puppies require carbohydrates for their rapid growth and high energy levels. As their bodies develop, they channel the energy derived from these nutrients into building muscle and enhancing overall body functions. Due to their active growth phase, a well-balanced diet with sufficient carbohydrates is essential.
Adult Dogs
The carbohydrate needs of adult dogs vary based on their activity levels. From typical house dogs to highly active working or sporting dogs, carbohydrates can help sustain their energy levels. House dogs benefit from balanced carbohydrate intake to maintain their weight, while active dogs need higher amounts for endurance and stamina.
Senior Dogs
As dogs age, their metabolic rate tends to slow down. Senior dogs require moderate carbohydrate levels to prevent unnecessary weight gain and manage their energy needs effectively. The goal is to provide them with enough energy while keeping their weight in check, thereby preventing age-related ailments like obesity.
Special Considerations for Active and Working Dogs
Active and working dogs have unique nutritional needs. These dogs are athletic or engaged in labor-intensive activities, so they require higher carbohydrate intake. The energy produced from carbohydrates helps these dogs sustain their activities over long periods, ensuring they remain agile and strong.
- Endurance and Stamina: High-energy dogs benefit from carbohydrates, which provide them the stamina needed for their daily exertions.
- Muscle Preservation: By supplying sufficient carbohydrates, the body can spare protein from being used as an energy source and instead use it for muscle repair and growth.
Balancing Carbohydrate Intake
Balancing the carbohydrate intake for dogs can be challenging but essential. The appropriate balance ensures they receive energy, maintain gut health, and don’t fall into the pit of over or undernutrition.
High-Carbohydrate Risks
- Obesity: Excessive carbohydrate intake can lead to weight gain and obesity. Overfeeding any nutrient without balancing energy expenditure will result in fat accumulation.
- Blood Sugar Spikes: Simple sugars and other high-glycemic carbohydrates can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, potentially leading to diabetes.
Low-Carbohydrate Risks
- Energy Deficiency: Not providing enough carbs, especially for active dogs, can lead to low energy levels, impacting their daily functions and activities.
- Muscle Breakdown: Without adequate carbohydrates, the body may use proteins for energy, leading to muscle depletion.
Ensuring a balanced carbohydrate intake tailored to your dog’s specific needs is paramount for their health and wellbeing. Adjustments should be made based on the dog’s life stage, activity level, and any specific dietary requirements.
Understanding the right nutritional guidelines and requirements will set the stage for discussing more intricate health considerations, such as managing diabetes and weight through diet.
Health Considerations and Management
Role in Managing Diabetes Through Low-Glycemic Carbohydrates
Diabetes in dogs, just like in humans, requires careful management to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Not all carbohydrates are created equal when it comes to their impact on blood sugar. This is where low-glycemic carbohydrates come into play.
Low-glycemic carbohydrates are those that break down slowly, leading to a gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. This slow digestion helps prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, which are crucial for diabetic dogs. Prime examples of low-glycemic carbohydrates include oats and barley. Including these in a diabetic dog’s diet can contribute significantly to maintaining steady blood sugar levels and overall health.
Weight Management Benefits Through High-Fiber Options
Managing your dog’s weight is crucial for their overall health, and high-fiber carbohydrates can play a significant role in this process. High-fiber foods help promote a sense of fullness, thus reducing the overall calorie intake without compromising on nutrition. This is particularly beneficial for overweight dogs or those prone to obesity.
Dietary fibers from vegetables and legumes such as pumpkins, carrots, and green beans are excellent for promoting satiety. Not only do these foods aid in weight management, but they also provide essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health.
Risks of Excessive or Inadequate Carbohydrate Intake
As beneficial as carbohydrates can be, the key is in moderation. Both excessive and inadequate carbohydrate intake can lead to various health issues in dogs.
Excessive Carbohydrate Intake
Feeding your dog too many carbohydrates can lead to obesity, especially if they have a sedentary lifestyle. Overconsumption can cause spikes in blood sugar levels, potentially leading to insulin resistance over time. Additionally, too much fiber can cause digestive issues such as bloating and can interfere with the absorption of other essential nutrients.
Inadequate Carbohydrate Intake
On the flip side, not enough carbohydrates in a dog’s diet can lead to low energy levels, especially in active or working dogs. When the carbohydrate intake is insufficient, the body starts relying on proteins for energy, which can result in muscle depletion, hampering the dog’s muscle repair and growth capabilities.
By understanding the right balance and choosing the appropriate types and sources of carbohydrates, you can ensure that your dog remains healthy and energetic. Up next, we’ll address common myths and facts surrounding carbohydrates in dog nutrition.
Common Myths and Facts
Addressing Misconception That Dogs Don’t Need Carbohydrates
One of the most prevalent misconceptions about canine nutrition is the belief that dogs do not need carbohydrates. This idea likely stems from the fact that dogs are descended from carnivorous ancestors. However, dogs have evolved significantly from their wild relatives. They are now classified as facultative carnivores, which means they can digest and utilize carbohydrates effectively for energy and other bodily functions.
Carbohydrates are not classified as essential nutrients by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO). However, they play a vital role in maintaining a dog’s overall health. Carbohydrates provide a readily available energy source, allowing proteins to be used for their primary functions such as muscle repair and growth, rather than being utilized solely for energy. In essence, while dogs can survive without carbohydrates, they can thrive with a balanced, carbohydrate-inclusive diet.
Clarifying That Grain-Free Isn’t Always Better
Another common myth is that grain-free diets are inherently better for dogs. While it’s true that some dogs may have specific grain allergies or sensitivities, this does not apply to all dogs. Grain-free diets were designed to help those specific dogs and are not necessarily better for the general canine population. In fact, grains such as brown rice, oatmeal, and quinoa are excellent sources of complex carbohydrates that provide sustained energy and support digestive health.
Switching to grain-free diets for dogs without grain allergies can sometimes lead to nutritional imbalances.
These diets often replace grains with other carbohydrate sources, like potatoes or legumes, that may not offer the same nutritional benefits. This misconception has led many pet owners to avoid grains unnecessarily, potentially missing out on their health benefits.
Explaining Relationship Between Carbohydrates and Obesity
A significant misconception is the idea that carbohydrates are a primary cause of obesity in dogs. While excessive carbohydrate intake can contribute to weight gain, it is essential to understand that obesity is generally the result of overfeeding and lack of adequate exercise. Carbohydrates, when consumed in appropriate amounts, actually play a role in weight management.
High-fiber carbohydrates, for example, promote satiety, which can help reduce overall calorie intake. Fiber-rich foods like sweet potatoes, pumpkin, and green beans can make dogs feel fuller for longer, thereby helping to prevent overeating. Additionally, complex carbohydrates, which break down more slowly than simple sugars, help regulate blood sugar levels, preventing energy spikes and crashes that can lead to increased hunger and overeating.
Balanced carbohydrate intake, tailored to the individual needs of the dog, is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight. Regular exercise and monitoring your dog’s overall caloric intake remain the most effective ways to prevent obesity.
Understanding these common myths and facts can help pet owners make more informed dietary choices for their dogs, ensuring they receive balanced nutrition suitable for their specific needs.









